In academic paper writing, students should adhere to the appropriate word count provided by the instructor.
In brief, the factors that influence the word count include academic level, subject area, research complexity and scope, research methodology, institutional requirements, and specific assignment instructions.
That being said, let us explore the general guidelines for research paper length, the role word counts play, the factors that influence length, and how to adjust word count while writing.
Role of Word Count in Research Papers
Word count has a lot of significance and purpose in research papers. First, it ensures that the paper remains clear and concise, whereby no tangential discussion or verbosity is used.
The word count also provides a pragmatic measure of the effort meant to be applied in completing a research paper. It helps students manage their time and resources well.
It also helps in standardization and comparability whereby research work can be evaluated consistently.
A word count enhances communication whereby a balance between being concise and providing adequate detail is maintained. This helps eliminate repetition and irrelevant information.
Finally, readers have particular expectations when it comes to the length of papers within a particular field. When you meet the word count, you meet the reader’s expectations and engage them well without making them feel underwhelmed or overwhelmed.
As noted, there is a strong connection between word count and effective communication. This is because expressing ideas succinctly and clearly without repetition or redundancy enhances communication.
Adhering to the word count enhances readers’ perception and engagement because they can navigate the paper assess its breadth and depth and finally evaluate its significance.
General guidelines for Research Paper Length
Research paper lengths may vary depending on various factors such as academic level, subject area, research complexity and scope, research methodology, and institutional and instructor requirements.

Though that is the case, it is common for research papers assigned to students to have specific word counts within particular ranges.
For example, when it comes to research papers meant for undergraduate students, the length is often between 2,500 to 5,000 words.
Such a word count only includes the main body of the research paper. The title page, table of contents, abstract, references, and appendices are usually excluded from the word count.
For postgraduate research papers, the expected length is usually longer and it is between 5,000 and 10,000 words. Students can even write more than 10,000 words.
The reason for this is that graduate-level research papers are more in-depth; meaning that there is more research, a higher level of critical thinking involved, and deeper analysis.
The field of study you are in while writing research papers also determines the word count.
For example, in social sciences like psychology, political science, and sociology, the length can be between 5,000 to 8,000 words. It may exceed 10,000 words for in-depth studies.
The length for natural sciences such as chemistry, biology, or physics is between 3,000 and 6,000 words for shorter papers and about 10,000 words for comprehensive studies.
Word counts for humanities like history, literature, cultural studies, or philosophy are between 6,000 and 10,000 words.
For engineering and computer science, the word count is between 4,000 and 8,000 words while medicine and health sciences range between 2,500 and 5,000 words.
Factors Influencing Research Paper Length
It is important to adhere to word count limitations and page restrictions to avoid academic consequences. The factors that influence the length of a research paper include:
1. Complexity and Depth of the Research

In-depth studies or research topics influence the length of the paper because they involve large datasets, multiple variables, and complex methodologies.
Such requires more words to fully explain and describe the process of research, findings, and discussions.
Though this is the case, it is important to provide sufficient information while being concise to avoid repetition and redundancy. Longer than usual papers overwhelm the reader.
Research areas within the fields of social sciences and humanities require longer papers while those in engineering and computer science, medicine and health sciences, and natural sciences require shorter papers because they require facts without a lot of explanations or examples.
2. Research Type and Methodology
This influences the length because quantitative or qualitative researches have different requirements.
Quantitative research requires detailed descriptions of statistical analysis and results while qualitative research involves extensive descriptions of observation, textual analysis, or interviews.
Empirical studies are longer because they involve quantitative research. Literature reviews and case studies may be shorter in comparison because they involve qualitative research.
However, it all depends on the field of study and the methodologies selected. Some methodologies that involve studying huge volumes of samples may require a lot of detailed descriptions, statistical analysis, results, and explanations.
3. Scope and Breadth of the Study
More in-depth studies require more words to adequately describe and explain the studies’ research process and findings.
When there is extensive data analysis and a comprehensive literature review, the word count will increase.
If you find that the scope of your research will compromise the length of the paper, only provide the most relevant points, data, and findings without any repetition or redundancy.
4. The Target Audience
The target audience can determine the length of your research paper. You have to understand your readership and their needs when it comes to reading your research paper.
Specialized audiences like a professor may require details because they already understand the subject matter and they want you to go deeper.
The general audience requires a brief paper that does not overwhelm them with detail.
5. The Quality and Quantity of Research Papers
The quality of your research paper is more important than its quantity (word count/length). While you are trying to meet the word count, be clear, concise, and well-organized to enhance readability.
Ensure that your paper has more substance instead of redundant and repeated information. As long as you organize your paper well, you will always meet the length requirements.
How to Adjust Word Count when Writing
1. Remove Redundancies
Eliminate any repetitive phrases or words that add no meaning. For example, you can say “bonus” instead of “added bonus”.
2. Avoid Passive Voice

Passive voice is wordier compared to active voice. Active voice is more succinct and direct.
3. Replace Phrases with Single Words
When you have phrases in your paper such as “bring into existence”, condense them using a single word such as “create”.
4. Combine Sentences and Paragraphs
If you review your paper and find that some sentences and paragraphs have related ideas, you can merge them to condense your paper.
5. Eliminate Phrases and Filler Words
You can remove words like “very”, just”, or “really”, and phrases like “due to the fact that” or “in order to” without changing the meaning.
How to meet Word Count Limits when Writing
Eliminate Unnecessary Words
Identify all extraneous words that do not add value or meaning to your content and remove them. This can be filler words, excessive modifiers, and redundant phrases.
Rephrase or Condense Sentences
If you have long sentences, rephrase or condense them while ensuring the message remains similar and concise. You may also combine sentences to shorten the word count.
Prioritize Key Points
Review your content and trim down those with less important details. Remove any irrelevant or tangential information.
Use Acronyms or Abbreviations
When appropriate, use abbreviations and acronyms for complex or long terms to reduce the word count. This depends on the context and your audience.
Avoid Excessive Details and Examples
Though important, do not overburden your paper with too many unnecessary details or examples. Only use the most relevant and impactful.
7 Strategies to Reduce or Expand the Content
1. Eliminating Irrelevant and Repetitive Information
Find any examples, details, or explanations that do not add value to their argument or main point and eliminate them to streamline your content.
You should also delete any repeated information.
2. Consolidate Similar Ideas
Identify sentences or paragraphs with related information and combine them.
3. Remove Filler Words and Phrases
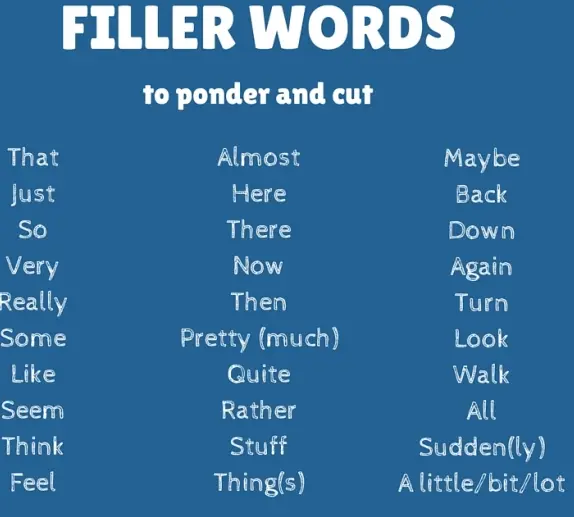
Review your content and remove any phrases or words that do not add value or meaning to your sentences.
4. Provide More Examples
Give your points and explanations more examples to support your arguments and give more examples.
5. Include Relevant Data or Statistics
Do more research and include more data and statistics to provide more evidence and strengthen your points.
6. Provide Counterarguments and Rebuttals
To make your paper more comprehensive, address the potential counterarguments and give rebuttals to reinforce your position.
7. Include Quotes and References
When needed, include quotes or references from reputable sources, studies, or experts to add depth and credibility to your content.
Situations where Strict Word Count Limitations Exist
1. Academic Writing
Academic institutions and instructors often specify the word limits for research papers and essays.
2. Newspaper and Magazine Articles
Publications have strict requirements for word counts because the content is meant to fit the available space.

3. Online Content
Blogs, websites, and other online platforms impose word count limits for posts, articles, and contributions.
This helps in search engine optimization (SEO), optimizes readability, and accommodates the attention span of the users.
4. Grant Proposal Application
Such applications specify the word count limitations for various sections like project description, methodology, impact statement, and budget.
5. Cover Letters and Resumes
These require applicants to adhere to specific word count limits to compel them to focus on the most impactful and relevant information.
This makes the hiring managers’ reviewing process efficient and easier.
6. Flash Fiction and Short Stories
Particular anthology submissions, literary journals, and competitions have strict limitations on word counts for flash fiction and short stories.
This challenges the writers to come up with compelling narratives within limited space.
Conclusion
Word counts play an important role in research papers. They vary depending on the academic level and field of the student.
The word count ensures that the paper remains clear and concise, provides a pragmatic measure of the effort meant to be applied in completing a research paper, and helps in standardization and comparability whereby research work can be evaluated consistently.
A word count also enhances communication and helps meet the reader’s expectations and engage them well without making them feel underwhelmed or overwhelmed.
Though adhering to word counts is important, it should be seen as a guide and not a strict rule.
Students and other writers should focus on the quality and not the quantity of their research papers. They should focus on clarity, coherence, and impactful communication.
